
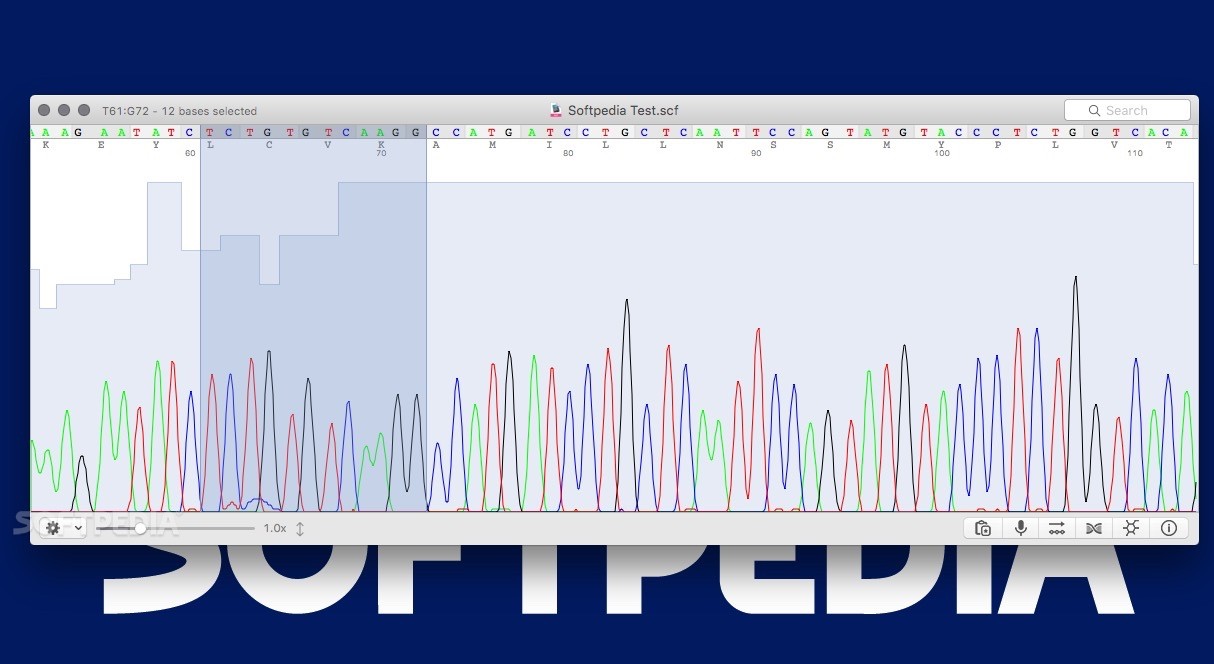
#Nucleobytes 4peaks code#
Conclusions: PIPEBAR and OverlapPER run on most operating systems and are freely available, along with supporting code and documentation, at and projects/overlapper-reads/. OverlapPER obtained the best results compared to currently used tools when merging 1,000,000 simulated paired-end reads. OverlapPER is a novel tool for overlapping paired-end reads accurately that accepts both substitution and indel errors and returns both overlapped and non-overlapped regions between a pair of reads. It is 7 times faster than Geneious and 14 times faster than SeqTrace for processing hundreds of barcoding sequences.
#Nucleobytes 4peaks software#
It is accurate as the proprietary Geneious tool and faster than most popular software for barcoding analysis. Results: PIPEBAR is a command line tool to automatize the processing of large number of trace files. We also proposed a paired-end reads assembly tool, OverlapPER, which is used in sequence or independently of PIPEBAR. To reduce at most such interaction, we proposed PIPEBAR, a pipeline for DNA chromatograms analysis of Sanger platform sequencing, ensuring high quality consensus sequences along with efficient running time. DNA barcode sequence analysis is usually carried out with processes and tools that still demand a high interaction with the user or researcher. DNA barcodes allow a rapid species discovery and identification and have been widely used for taxonomic identification by targeting known gene regions that permit to discriminate these species.

These materials provide ideas for developing bioinformatic experience in the classroom.īackground: Taxonomic identification of plants and insects is a hard process that demands expert taxonomists and time, and it’s often difficult to distinguish on morphology only. Phylogenetic trees – the core set of methods for comparing DNA sequences. ‘Metagenomic’ studies – newer, studies sampling all DNA in environments (or filtering to include only bacterial DNA, for example) – allow gene function and patterns of abundance to be considered D. ‘Gene barcoding’ - directed sequencing of a gene for classification - applied to all life, including microbes C. Generation and assembly of DNA (typically) sequences B. Some important concepts in the field of ecological bioinformatics are: A. Bioinformatics has influenced the way we study biodiversity – for example in the phylogenetic recognition of species (all Kingdoms), and in studying bacteria and viruses which cannot be grown in the lab. The future could potentially involve personalized genome medicine. The scope for bioinformatics is increasing dramatically. There is abundant information and tools (very often free) that mean that students can become involved in ‘data mining’, perhaps setting up there own biological questions within a bioinformatics teaching experience. computer literacy, report writing, project planning, hypothesis testing, and group based work). Teaching Bioinformatics particularly complements ecology and genetics concepts, as well as many other areas of expertise (e.g. Bioinformatics is being used more in the field of ecology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
